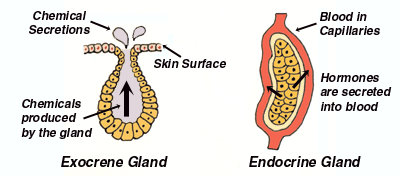
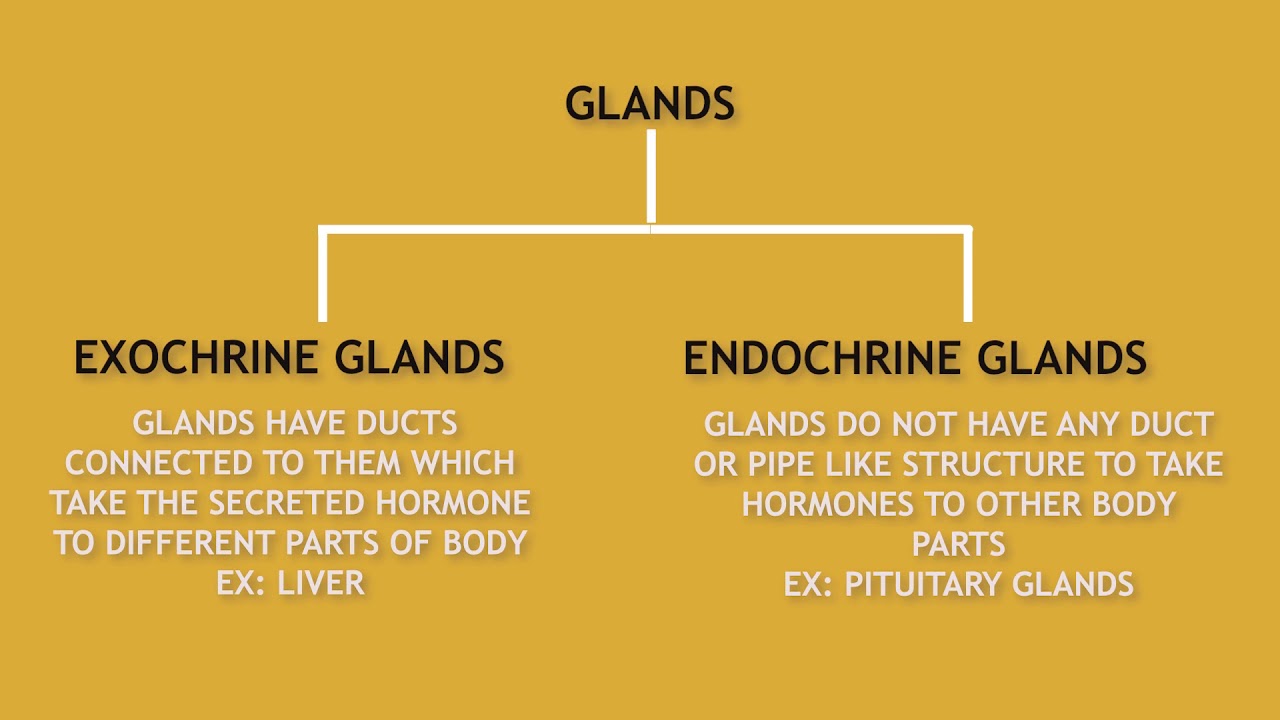
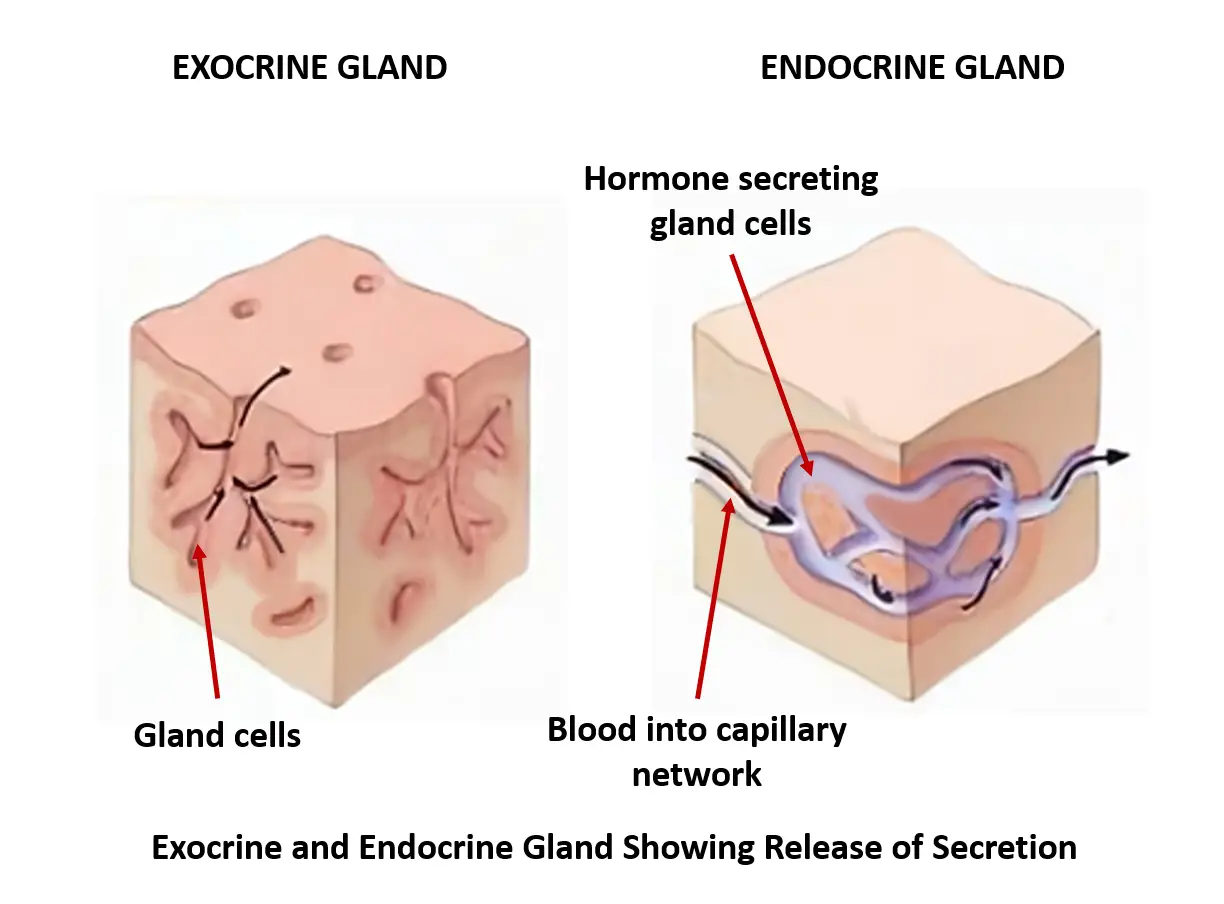
(2 marks) Ans Exocrine gland is a gland that pours its secretion on the surface or into a particular region by means of ducts for performing a metabolic activity, eg, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, salivary glands and intestinal glandsExamples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, and mucousExocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstreamThe exocrine glands They are a type of gland that secrete their products through ducts that open towards the external surface of the body or towards the epithelial surface, external or internal, of the epithelium that gives rise to them A gland is a functional unit of cells that work together to synthesize and release a product in a duct or
Do Any Of The Exocrine Glands Produce Hormones Socratic
Types of exocrine glands secretion
Types of exocrine glands secretion-Thus the two types of glands are called Exocrine and Endocrine All exocrine glands are glands with ducts The secretions are delivered into ducts and end up on the epithelial surface For example, the sweat glands are exocrine glands Holocrine secretion is a specific mode of secretion involving secretion of entire cytoplasmic materials with remnants of dead cells, as observed in multicellular exocrine glands of reptiles, birds, and mammals What are the 3 types of exocrine glands?




Solved Exocrine Glands Release Secretions Onto The Surface Chegg Com
They are saclike structures consisting of secretory tissue There are two main types of glands as the Exocrine glands Salivary, mucous, lachrymal, pancreatic, ceruminous glands ie sweat glands, and mammary glands Endocrine glands Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal gland, thymus gland, etcThere are two main types of glands → exocrine glands The exocrine glands release the secretion on the free surface (body surface or organ light) and present channels or ducts through which the secretion passes until it reaches the place where it will be eliminated In these glands it is possible to observe two distinct parts aIn this video we look at the different types of glands in the body We discuss the structure of glands and how they are classifiedTranscript/notesGlands are
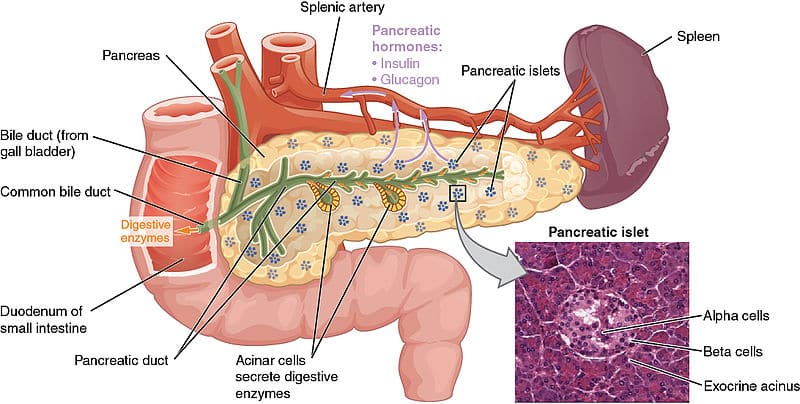
The exocrine pancreas and certain salivary glands of mammals secrete a variety of enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract, where they digest food The same glands also release these enzymes into the bloodstream This latter process has commonly been assumed to occur solely as the result of aObjectives •Identify every epithelium present in any tissue section •Differentiate between mucus and serous secreting epithelia •Identify singlecelled glands, endocrine glands and the various types of exocrine glands •Detail the structure of the sebaceous gland •Identify the different types of sweat glands and distinguish the duct from the secretory regionObserve the different ways to eliminate secretion * Like example of exocrine glands, we can mention the mammary, sweat and sebaceous glands → endocrine glands The endocrine glands eliminate their secretion directly into the bloodstream and, unlike the exocrine glands, they do not have a glandular duct
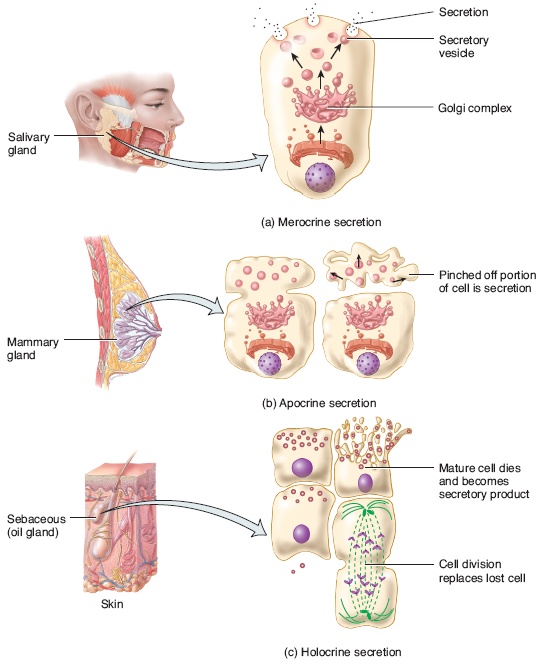
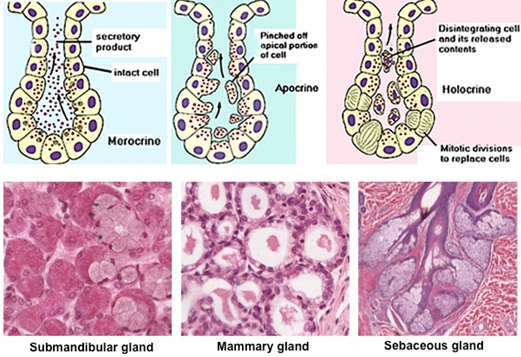
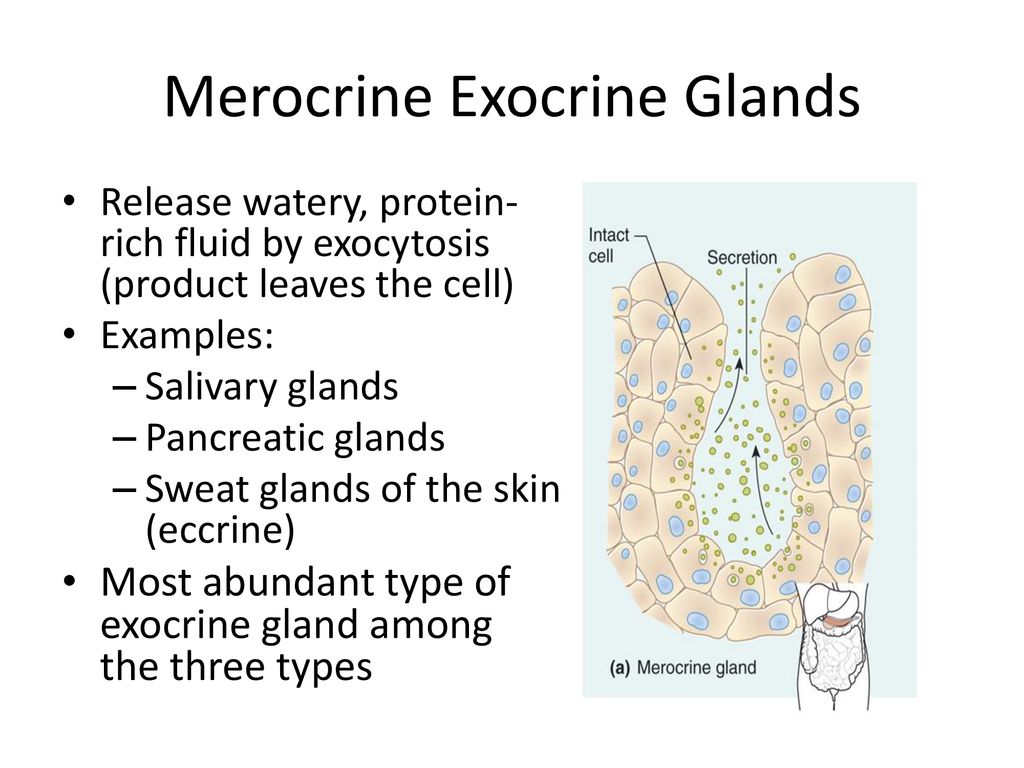
Exocrine glands can be classified by their mode of secretion and the nature of the substances released, as well as by the structure of the glands and shape of ducts Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the contents are released by exocytosisThe three types of exocrine glands are Holocrine Glands Merocrine Glands Apocrine Glands Similarly, it is asked, what is exocrine and endocrine glands and give examples? The most prominent exocrine glands are sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and mammary glands Exocrine glands also store digestive enzymes in the intestine Two types of exocrine glands can be identified based on the complexity of glands They are unicellular exocrine glands and multicellular exocrine glands




Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Medical Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



2
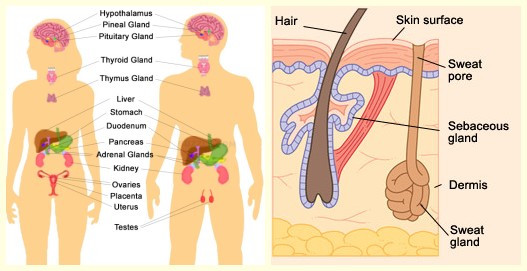
Secretion of hormones is usually regulated by negative feedback, where a rise in the level of hormone in the blood decreases its secretion Sebaceous glands Sebaceous glands are simple, branched, acinar, exocrine glands located within the skin They secrete a fatty substance sebum, into the follicular duct, which surrounds the hair shaftThe glands which pour their secretions on the epithelial surface, directly or through ducts are called exocrine glands (= extemally secreting glands) These include salivary glands, gastric glands, intestinal glands, tear glands, sweat glands, oil glands, mammary glands, etcExocrine glands are cellular substructures, organs, in a body that provide a system to secrete substances out and external to the body They are distinct from the other type of gland, endocrine, in that exocrine gland secretions end up external to the body, while endocrine secretions go into the bloodstream/internal Similarly, what are the 3




Do Any Of The Exocrine Glands Produce Hormones Socratic




Types Of Multicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet
Name two examples of each exocrine and endocrine glands An exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of Exocrine system is one of the two types of gland systems in our body It is a collection of glands Exocrine system produces and secretes substances that are necessary to protect and lubricate the human body Exocrine glands are composed of aTypes of Glands Exocrine Glands are those which release their cellular secretions through a duct which empties to the outside or into the lumen (empty internal space) of an organ These include certain sweat glands, salivary and pancreatic glands, and mammary glands They are not considered a part of the endocrine system



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology




Endocrine System 1 Overview Of The Endocrine System And Hormones Nursing Times
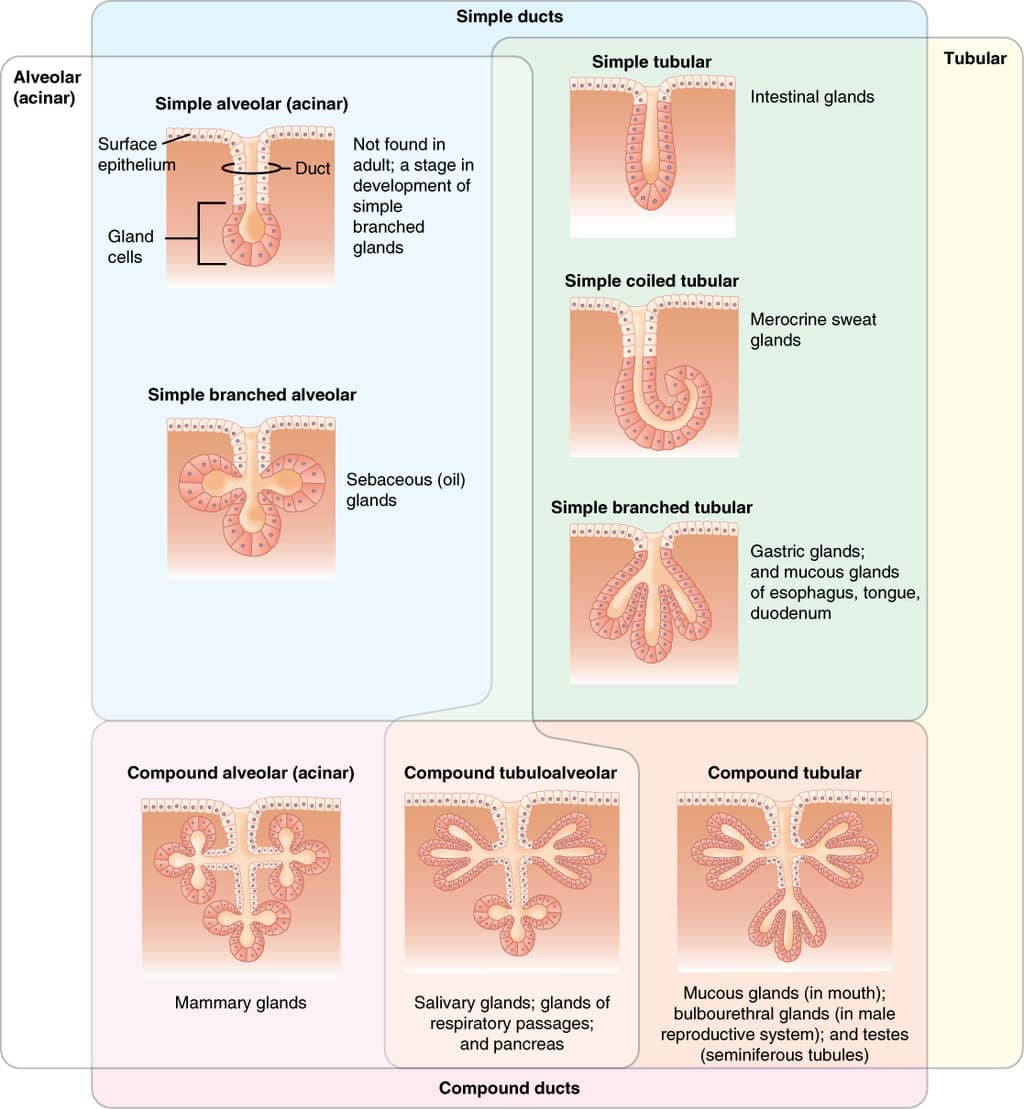
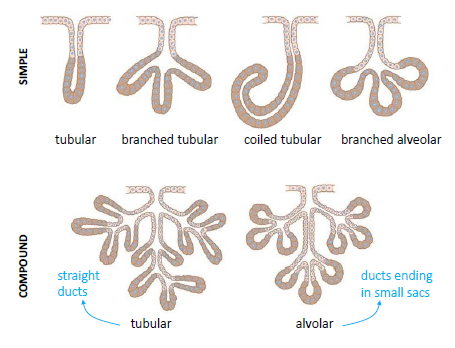
Exocrine glands can be classified by their mode of secretion and the nature of the substances released, as well as by the structure of the glands and shape of ducts (Figure 410) Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the Two principal types of glands exist exocrine and endocrine The key difference between the two types is that, whereas exocrine glands secrete substances into a ductal system to an epithelial surface, endocrine glands secrete products directly into the bloodstream 1The lacrimal gland is an exocrine gland in the anterior aspect of the supratemporal orbit within the bony lacrimal fossa The majority of the gland lies within this fossa, but the lateral horn of the levator palpebrae superioris separates this orbital part from the palpebral lobe, which extends anteriorly into the supratemporal conjunctival cul




10 Histology Of The Salivary Glands And The Exocrine Pancreas Flashcards Quizlet




Merocrine Wikipedia
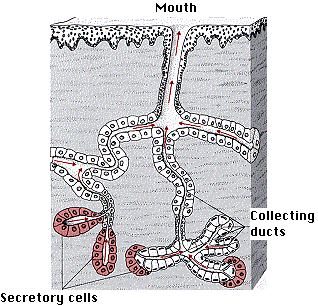
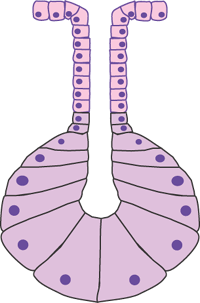
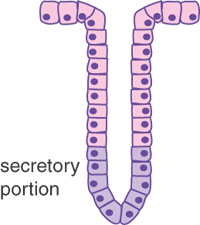
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ductsHumans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual) as well as hundreds of minor salivary glandsSalivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous or seromucous (mixed)11 rows Exocrine secrete into a location or region of the body through a duct and their secretions areClassify the major exocrine glands with respect to their structure and modes of secretion Give clear examples of where each class of gland would be found in the human body



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Definition Types Features Functions




Classification Of Glands Youtube
The glands are of two types based on the mode in which they are released or secreted Endocrine glands These are ductless glands (no tube to carry to various parts) Their secretions are directly released into the blood which carries them to various parts of the body Exocrine glands The exocrine glands have ducts **Please note that merocrine, apocrine and holocrine are all distinguished types of exocrine glands ** Exocrine glands secrete their products in duct system as happens in case of enzymes, milk, sebum or sweat This is different from the mode of secretion seen in ductless endocrine glands, which release their products (mainly hormones) directly in blood streamExocrine glands secrete enzymes, ions, water, mucins and other substances
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2472/r3yQf6wxyufP1joSAhl7eg_Mixed_seromucous_glands.png)



Glands Anatomy And Clinical Notes Kenhub




Pin On School
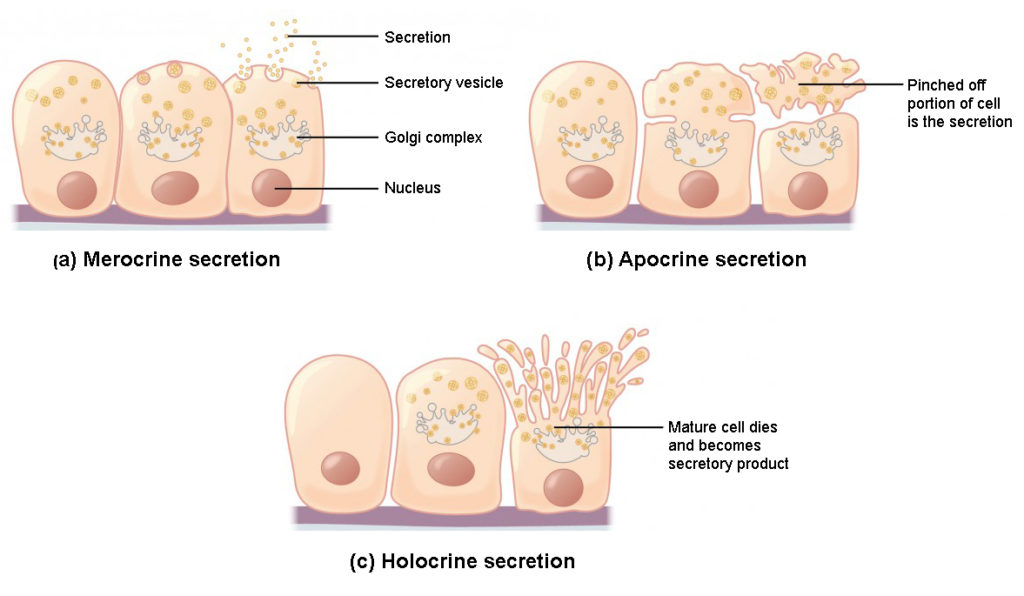
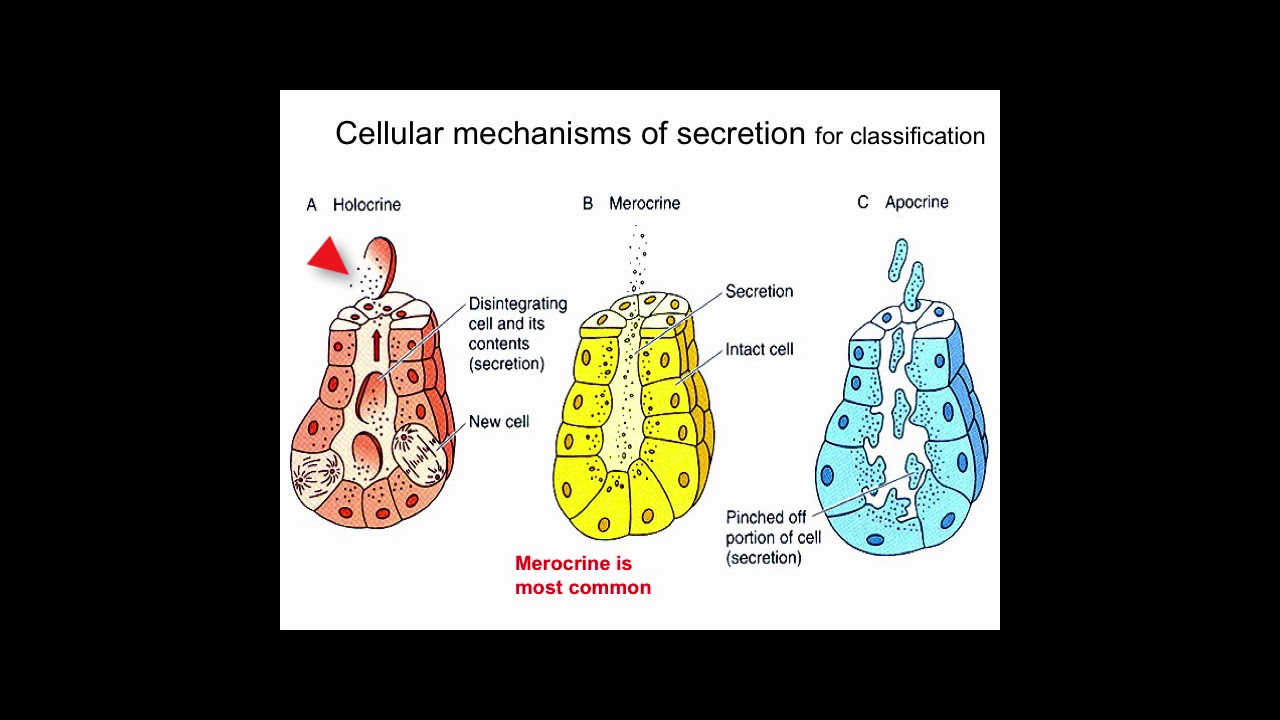
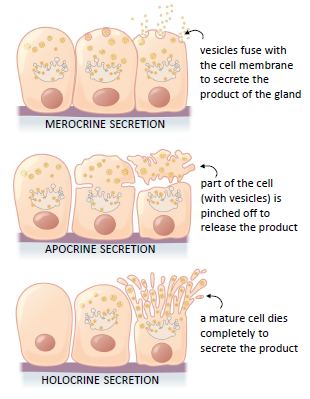
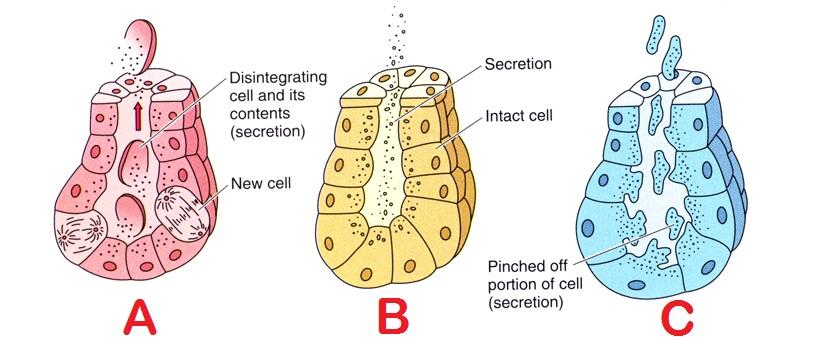
There are three different ways in which exocrine glands secrete their products These modes of secretion are called merocrine, apocrine, and holocrine Merocrines glands (eg, salivary glands) secrete their product from intact cellsLocation pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid and parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, thymus, ovaries and testes exocrine glands Secretory products are released into ducts that empty onto the epithelial surfaceExocrine glands secrete enzymes, ions, water, mucins and other substances into the digestive tract The glands are situated within the gastrointestinal tract, in the walls of the stomach and intestines, or outside it (salivary glands, pancreas, liver, see above) Secretion is under the control of nerves and hormones



1




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll
Cellular Exocrine glands are comprised of an acinus and a duct with different cell types, respectively These glands are found in many organs within the body and demonstrate a large variety in the function of their secretions As such, a wide range of cell types exists in exocrine glandsExocrine Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 Function Secrete productions through ducts Examples Sweat, salivary, sebaceous, von Ebner's glands Secretions Sweat, saliva, sebum, digestive enzymes Click again to see term 👆 Tap again to see term 👆 Nice work! Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion Holocrine secretion involves the release of whole cells such as release of spermatozoa from the testes or the breakdown of an entire cell to form the secretion such as release of sebum in sebaceous glands




Lecture 9 Histology Of Glands Flashcards Quizlet



How Are Exocrine Glands Classified Socratic
The human body has many glands which produce many secretions, such as sweat, saliva, oil and hormones Anatomically, these glands are broadly classified into two types based on the presence or absence of ducts Endocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, while exocrine glands secrete hormones through ductsExocrine Glands Exocrine glands have ducts and they secrete onto a surface examples of exocrine glands are sebaceous and sweat glands (in the skin), salivary glands (oral), Brunner's glands So, we have covered their basic structure and function in tissue types, and we have looked at several examples of exocrine glands in other topicsThe apocrine glands release a portion of their own cells One may also ask, how many exocrine glands are there?



Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology I




5 1 Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Secrete Substances Composed Of Epithelial Tissue Exocrine Glands Connect To Surface With A Duct Epithelial Tube Endocrine Ppt Download
The substance types created by exocrine glands varies wildly and includes tears, sweat, milk, enzymes, bile, etc Exocrine and Endocrine Function of Pancreas Some glands are Exocrine glands can also be classified into a variety of categories in terms of their function They can be categorised into 3 subtypes according to their type of secretory product Serous glands Mucous glands Mixed glands Serous glands produce serous fluid, a watery substance containing enzymesThe three types of exocrine glands are Holocrine Glands Merocrine Glands Apocrine Glands Similarly, it is asked, where do exocrine glands release hormones?



9 Endocrine System Biology4isc




Exocrine Gland Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Exocrine glands are cellular substructures, organs, in a body that provide a system to secrete substances out and external to the body They are distinct from the other type of gland, endocrine, in that exocrine gland secretions end up external to the body, while endocrine secretions go into the bloodstream/internalThe three types of exocrine glands are Holocrine Glands Merocrine Glands Apocrine Glands Exocrine glands are classified as merocrine, apocrine and holocrine, depending on their mode of secretion All these are able




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll




Exocrine Glands Of The Integumentary System Youtube
The secretion is usually done through a duct directly to the apical surface of the epithelium where the gland is located The exocrine glands are subdivided into three types or groups Apocrine glands are exocrine glands that lose part of their cytoplasm and its membrane to form extracellular vesicles that transport secretion For example Exocrine Glands Vs Endocrine Glands Definition, Types, Functions and Differences by admin Glands are a group of cells or organs of the human or animal body which play an important role to secrete particular chemical substances for various body functions Ques What are Endocrine and Exocrine glands?




File Endocrine Vs Exocrine Svg Wikimedia Commons



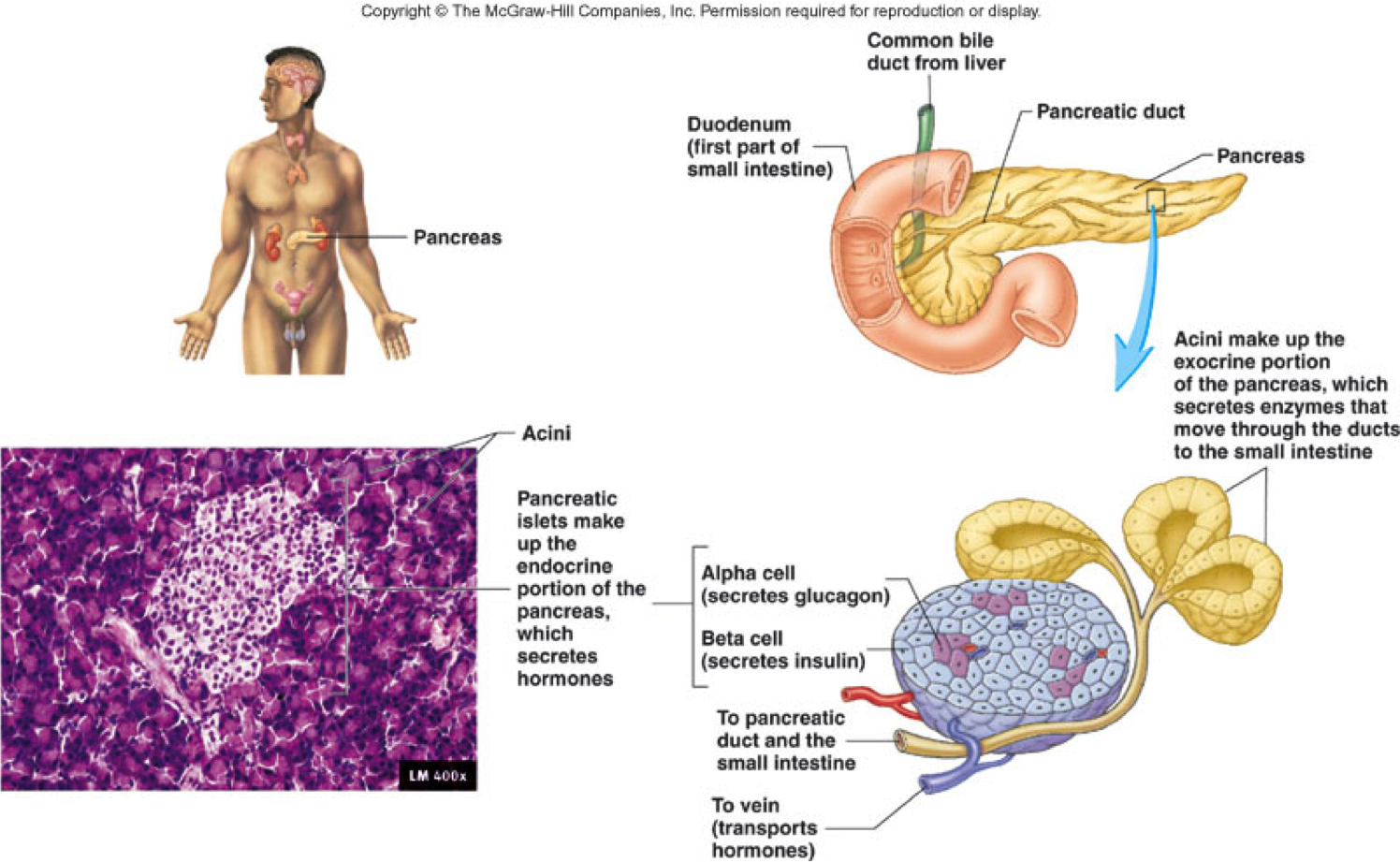
The Exocrine Pancreas Function Secretion Regulation
9596 Anatomical terminology Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous




Exocrine Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Is The Parathyroid An Endocrine Gland Are Sweat Glands Endocrine Glands Socratic




Differences Between Endocrine Glands And Exocrine Glands



Exocrine Glands




Gland Definition Types Examples And Quiz Biology Dictionary



Exocrine Glands Youtube




Methods Of Secretion Physiology Americorps Health



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide




Glandular Epithelia Exocrine Glands Can Be Classified By Structure Of Gland Type Of Secretion Produced Mode Of Secretion Endocrine Glands Secretes Ppt Download



Glands What Are Glands Types Of Glands Merocrine Glands Apocrine Glands Holocrine Glands Youtube




Exocrine Gland Ppt Download



Exocrine Gland And Endocrine Glands Youtube




Overview Of Exocrine Gland Physiology Pancreatic And Salivary Glands The Gastrointestinal System Medical Physiology 3rd Edition




ป กพ นในบอร ด Chapter 5 Histology




5 1 Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Secrete Substances Composed Of Epithelial Tissue Exocrine Glands Connect To Surface With A Duct Epithelial Tube Endocrine Ppt Download
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2471/shYLtWdYUjK3qRvwMzK4Q_Compound_tuboalveolar_mixed_salicary_gland.png)



Glands Anatomy And Clinical Notes Kenhub




Exocrine Glands Bioninja



Glands And Its Types Glands A Cell Tissue Or Organ Which Secretes Specific Biology



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy




Exocrine Gland Wikipedia



Sweat Gland Wikipedia



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Exocrine Gland Ppt Download



Exocrine Glands




Types Of Exocrine Gland Secretion Chromoscience



Hormones Secretion Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Youtube




Glands Hormones Oestrogen Glucagon Adrenaline Insulin Testosterone Syllabus



Epithelia The Histology Guide
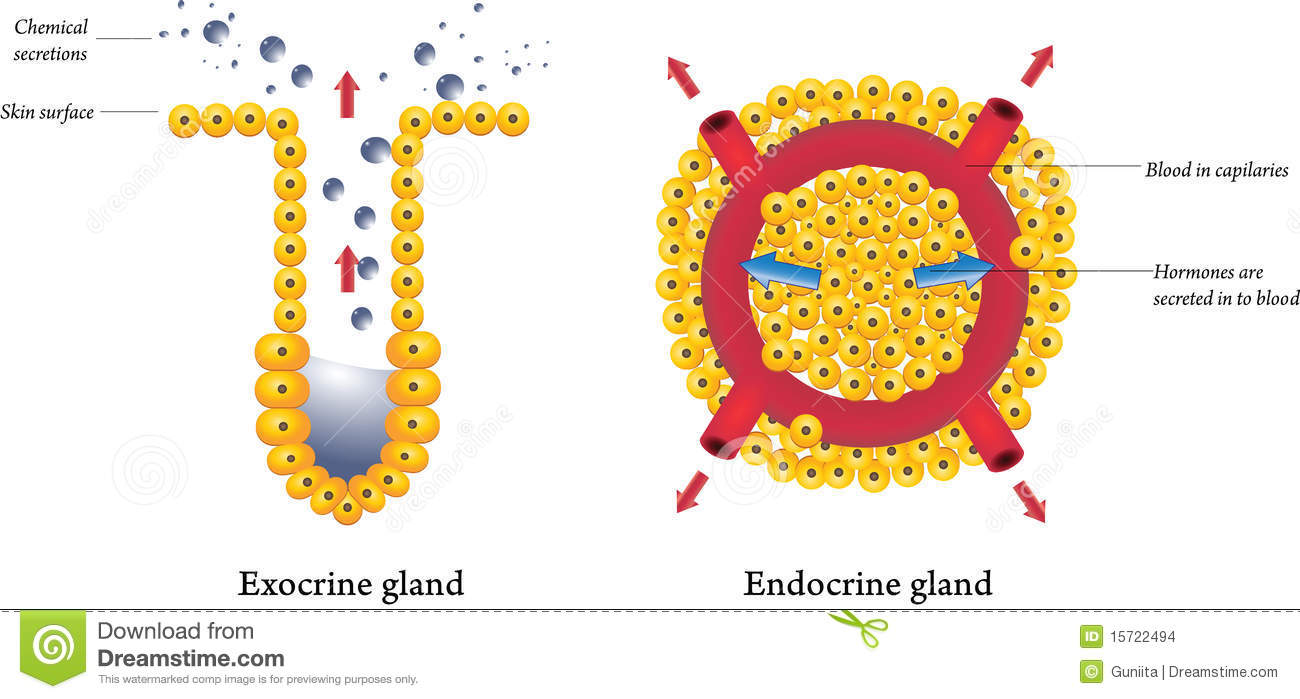



Do Endocrine Glands Secrete Hormones Directly Into The Bloodstream Socratic
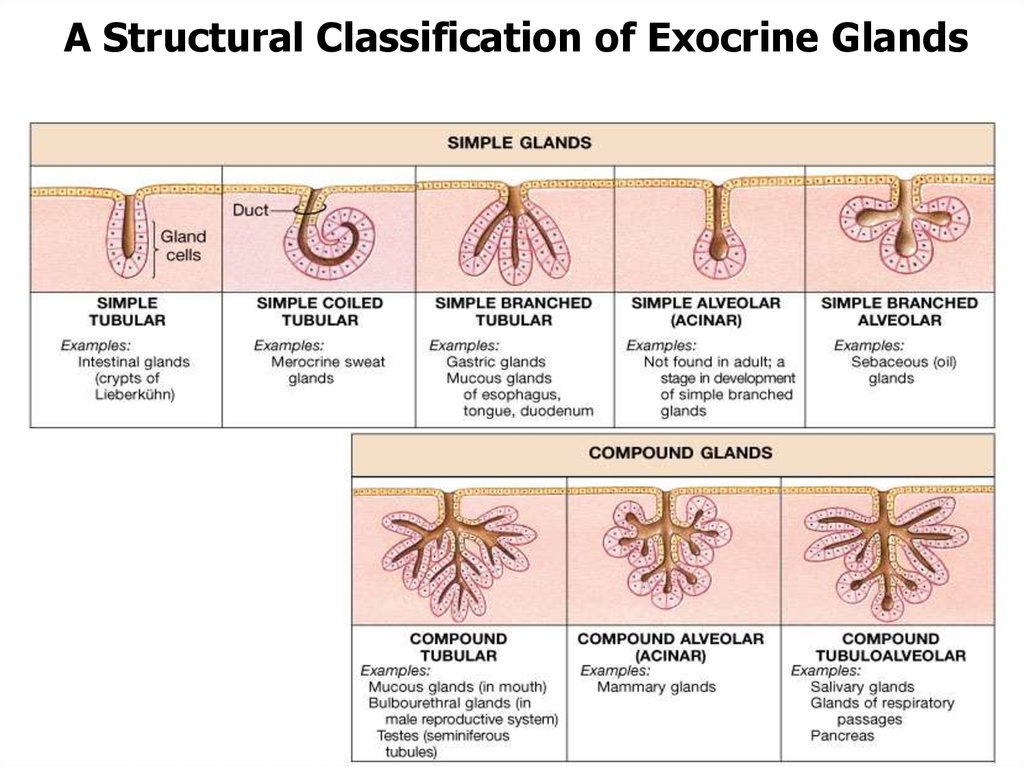



Cytology Embryology General Histology Online Presentation




Glandular Epithelia Exocrine Glands Can Be Classified By Structure Of Gland Type Of Secretion Produced Mode Of Secretion Endocrine Glands Secretes Ppt Download




Glandular Epithelium A Gland Is A Single Cell Or A Mass Of Epithelial Cells Adapted For Secretion Classification Of Glands By Destination By Structure Ppt Video Online Download




Exocrine Glands Histology Lecturio Youtube
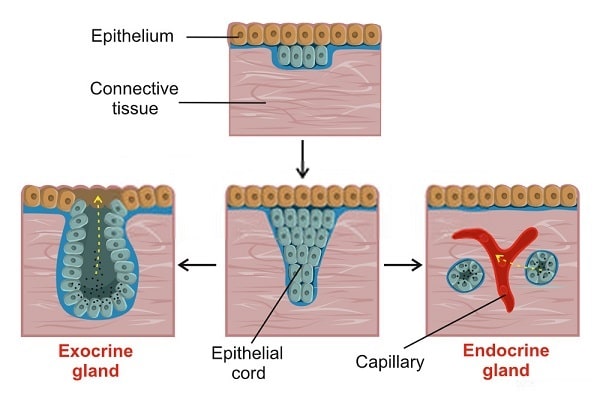



15 Types Of Glands In Human Body Their Functions




Glandular Epithelium Composed Of Cells That Are Specialized To Produce And Secrete Substances Into Ducts Or Into Body Fluids Such Cells Ppt Download



Skin The Histology Guide
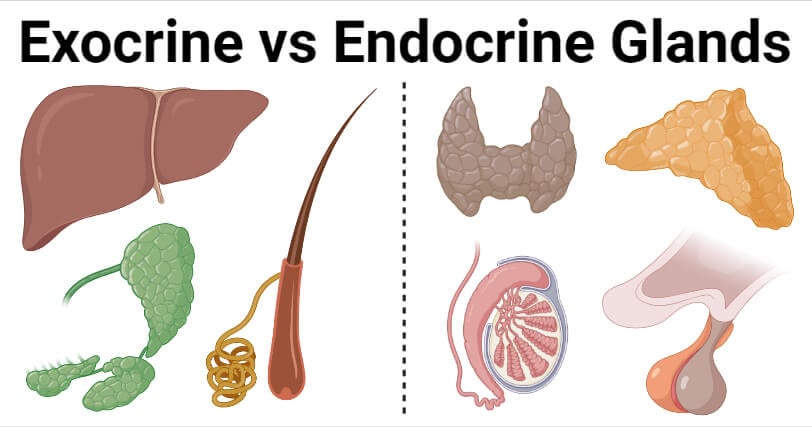



Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Definition 8 Differences Examples




Exocrine Gland Structure Physiology Americorps Health



Glandular Epithelia Endocrine Glands Secretes Hormones Into Directly




Solved Exocrine Glands Release Secretions Onto The Surface Chegg Com
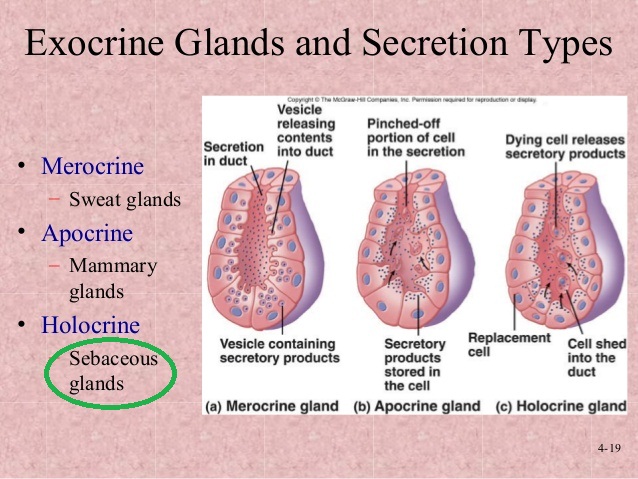



Is A Sebaceous Gland Apocrine Holocrine Or Merocrine Socratic
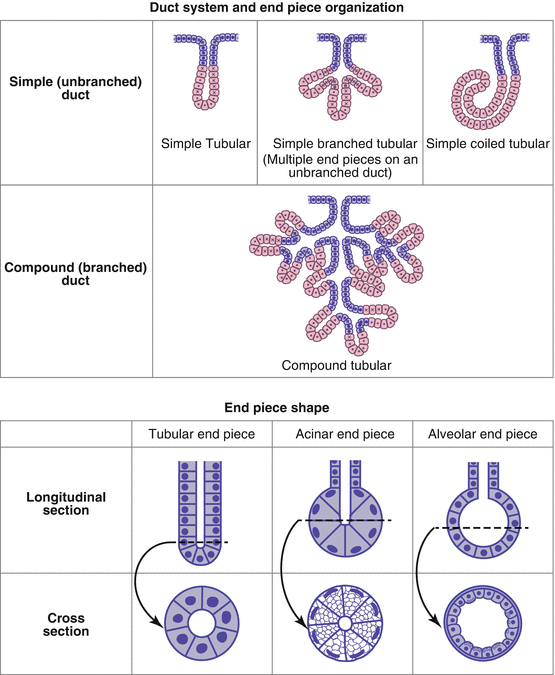



Glandular Epithelium And Glands Springerlink



Tissues And Membranes




Pin On Chapter 5 Histology




Endocrine System Glands 2 Types 1 Exocrine Gland Ducts Lumen And Surfaces 2 Endocrine Gland No Ducts Secrete Chemical Messengers Called Hormones Ppt Download




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll



How Are Exocrine Glands Classified Socratic
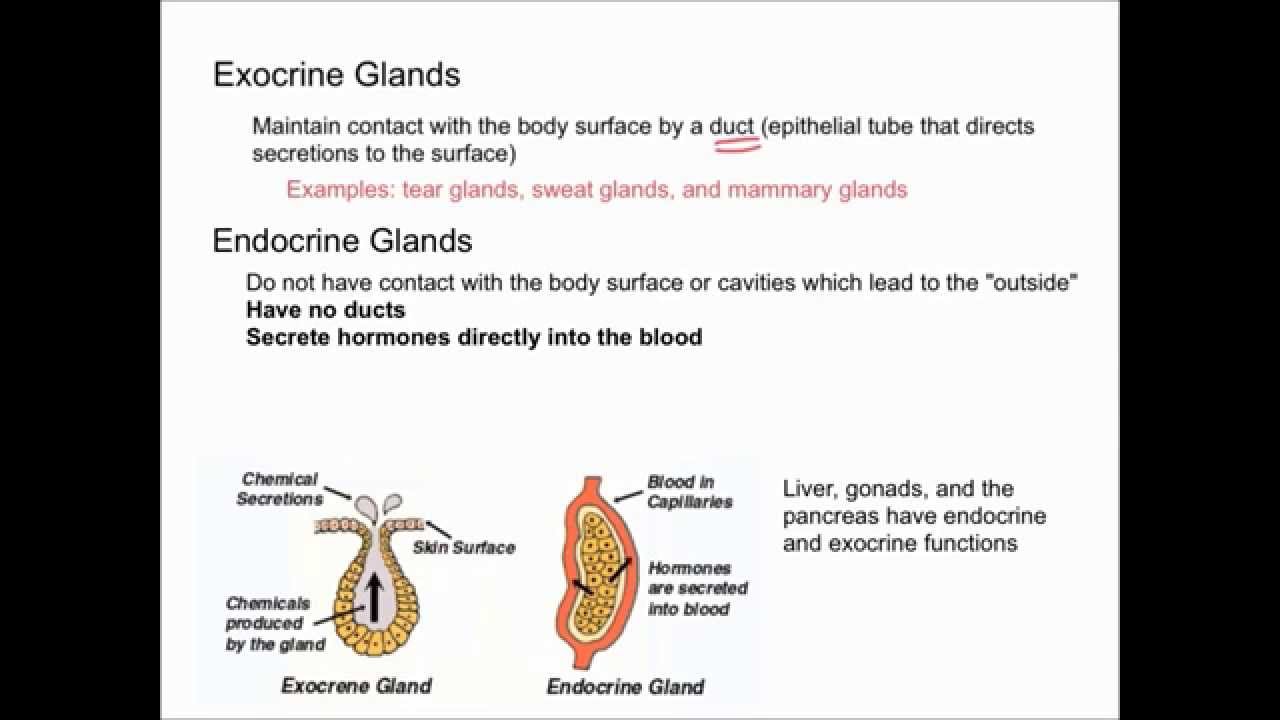



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Youtube




Pin On Epithelial Tissue




Lecture 9 Histology Of Glands Flashcards Quizlet



1




Holocrine Wikipedia



Classification Of Exocrine Glands Type Of Secretions Produced




Introduction Types Of Glands Classification Functions Of Glands Ppt Download



Lecture 21




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll




Methods Of Secretion Physiology Americorps Health




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams
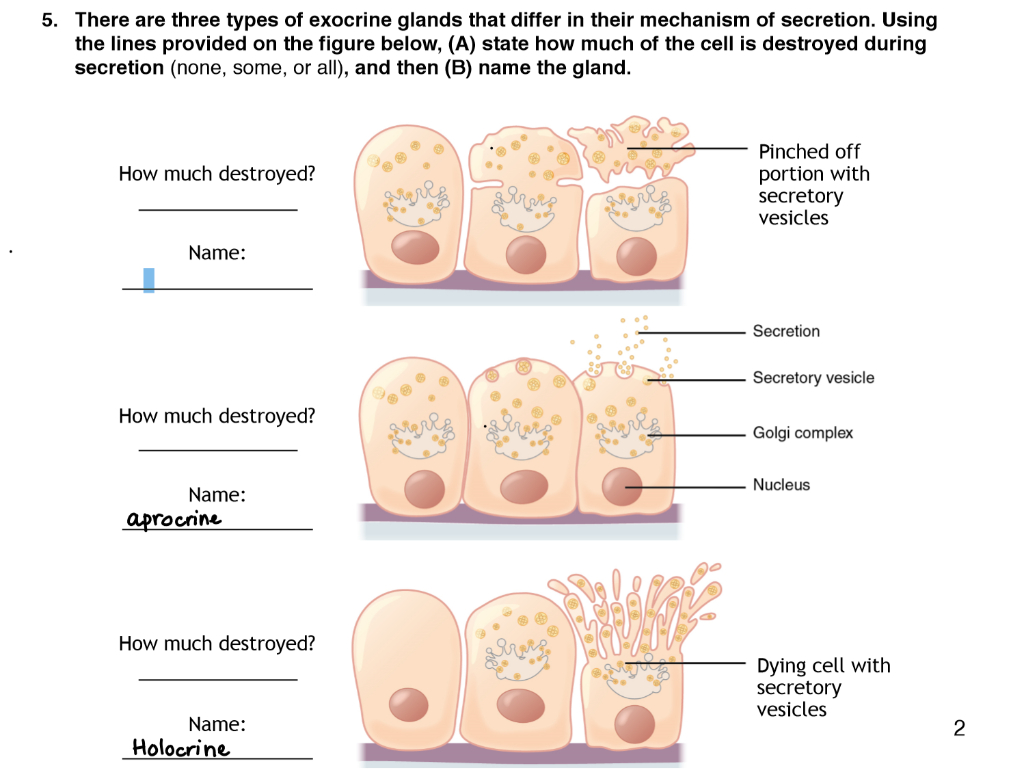



Solved 5 There Are Three Types Of Exocrine Glands That Chegg Com
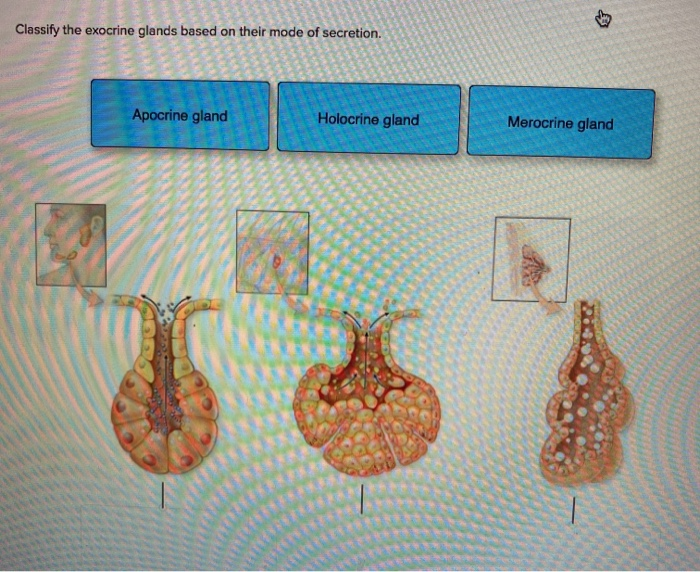



Solved Classify The Exocrine Glands Based On Their Chegg Com



3
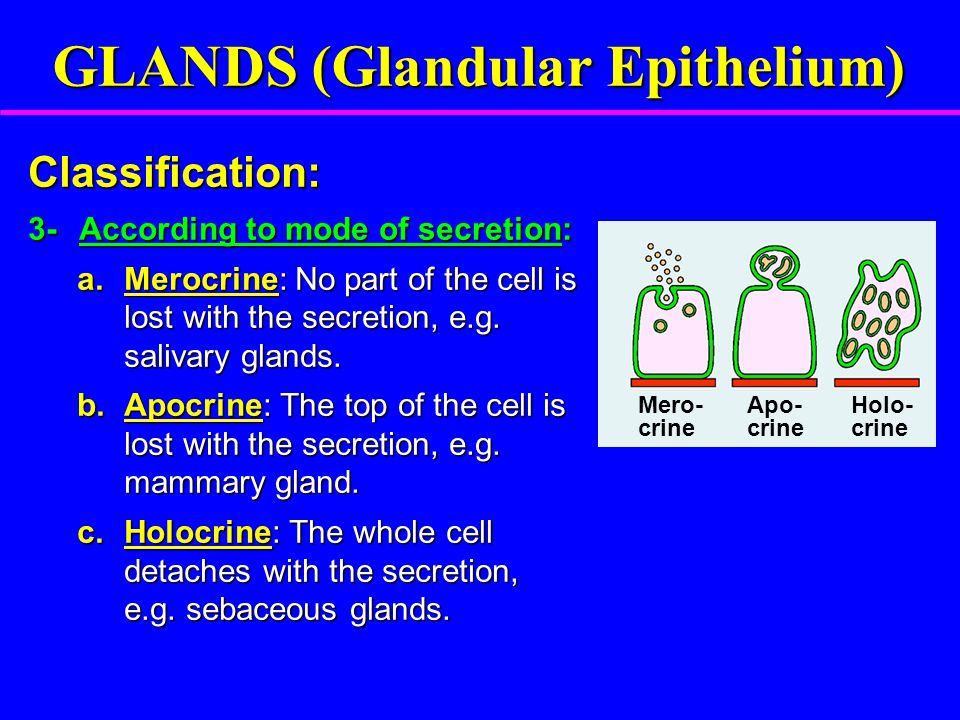



How Do Apocrine Exocrine Merocrine And Holocrine Glands Differ Socratic




Glandular Epithelia Exocrine Glands Can Be Classified By Structure Of Gland Type Of Secretion Produced Mode Of Secretion Endocrine Glands Secretes Ppt Download
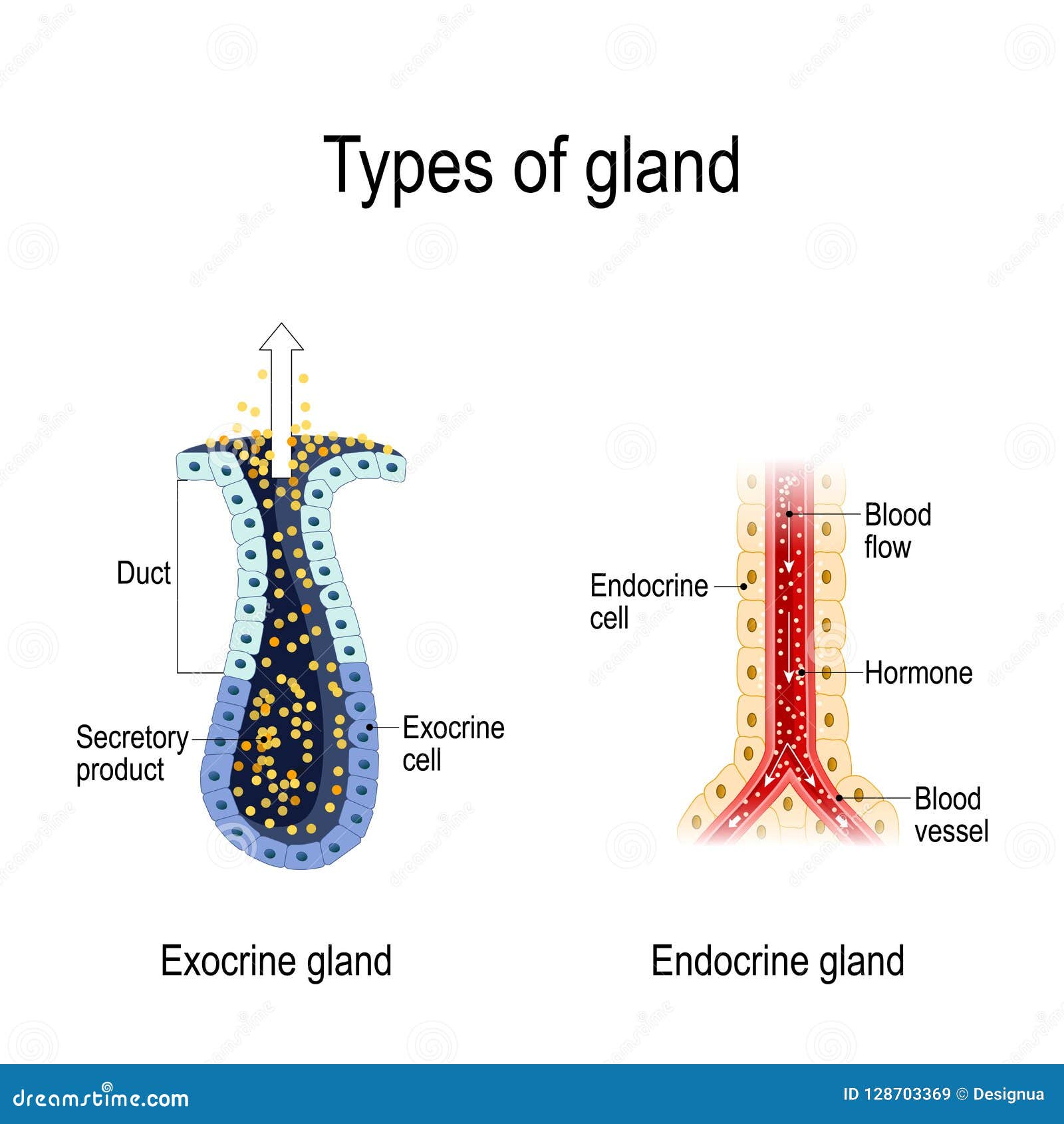



Anatomy Of An Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Stock Vector Illustration Of Blood Cross



What Is An Example Of An Apocrine Exocrine Merocrine And A Holocrine Gland Socratic



Epithelia The Histology Guide



Exocrine Vs Endocrine What Is The Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine You Ask We Answer




Glands Hormones Oestrogen Glucagon Adrenaline Insulin Testosterone Syllabus



1




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll




Exocrine Glands




Epithelial Gland Types Endocrine Exocrine Sweat Glands Stock Illustration Illustration Of Deliver Illustrations



Animal Tissues Epithelial Tissue Glands Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology



Glandular Epithelium Made Of Cells That Secrete Substances Into Ducts Or Body Fluids Almost Always Columnar And Cuboidal Epithelia Exocrine Vs Endocrine Ppt Download




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams




Power Point Lecture Slides Prepared By Barbara Heard




Sox10 Regulates Plasticity Of Epithelial Progenitors Toward Secretory Units Of Exocrine Glands Sciencedirect



2



Exocrine Gland Liberal Dictionary




Glands Hormones Oestrogen Glucagon Adrenaline Insulin Testosterone Syllabus



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿